Image credit: Unsplash
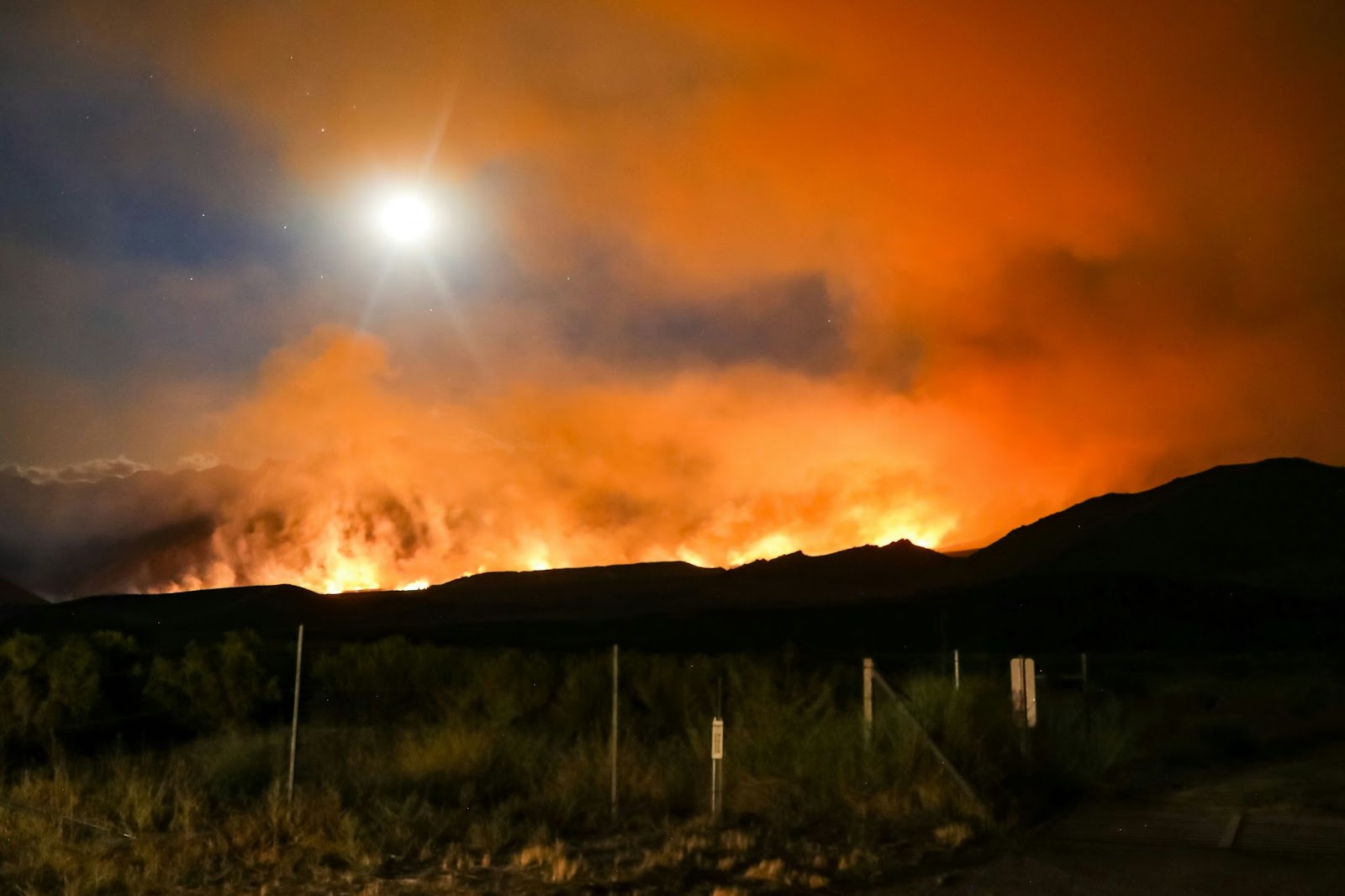
Greenhouse gas emissions have far-ranging environmental and health effects that have been raising concern in recent years for the significant, long-lasting impacts they could have on you and the world. Essentially, greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and certain synthetic chemicals, are trapping some of the Earth’s energy, retaining heat in the atmosphere, and influencing weather and climate patterns worldwide. Much of these emissions are proven to be at the hands of humans. While California is known as a climate-forward-thinking state, they are also the number one contributor to most of the little-known gas sulfuryl fluoride.
The Rise and Risks of Sulfuryl Fluoride
Regulators first approved sulfuryl fluoride for use in pesticides in 1959, unaware of its lengthy atmospheric lifetime. Thus, unfortunately, there was no forward movement in studying the environmental impacts of this synthetic pesticide, and this potent greenhouse gas has been filling up Earth’s atmosphere with its high global warming potential.
Flying under the radar for decades, researchers are now more aware of sulfuryl fluoride’s significant environmental impact because the synthetic pesticide has become more widely used. Research has shown the impact of this little-known gas can be up to 7,500 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of its greenhouse gas impact. Johns Hopkins University study co-author Dylan Gaeta believes recent research proves the urgent need for regulatory action, stating, “Without some form of intervention, sulfuryl fluoride is going to keep accumulating in our atmosphere.”
A recent study has shown that California is the biggest culprit of sulfuryl fluoride emissions among all other U.S. states, with the highest in the southern coastal areas of California (Los Angeles, Orange, and San Diego counties). This study traced a whopping 85% of all U.S. emissions of sulfuryl fluoride to The Golden State, whose $4.2 billion pest control industry uses it for dry wood termite control.
Health and Environmental Concerns
Primarily used in structural fumigation, researchers described the process as turning homes and other structures being fumigated into a “circus tent.” When the fumigation is complete, all the hot air inside is released into the atmosphere—and this “hot air” is proving to be increasingly unsafe. Gaeta argues, “It doesn’t have the same ozone-depleting problem as methyl bromide, but it has a long lifetime in the atmosphere, so over that period, it acts as a potent greenhouse gas.”
The Need for Action
With the rising concern of toxicity entering and lingering in the air, this synthetic pesticide manifests detrimental health issues for people, with short-term exposure linked to respiratory ailments, seizures, stomach pains, and other nervous system problems; addressing this greenhouse gas emission is becoming critical – but California is not entirely on board with bringing the lethal gas down.
A 2022 petition from the Center for Biological Diversity called for the phase-out of sulfuryl fluoride, a petition that the California Air Resources Board ultimately rejected. While the state has set a goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 48 percent of the 1990 levels by 2030, the board rejected the petition, claiming the agency “lacks sufficient information at this time to determine whether a sulfuryl fluoride phase-out is warranted given its use and overall impact on global temperature changes.”
California can start tackling the impact of this greenhouse gas emission on the atmosphere. Sulfuryl fluoride is a deadly pesticide being released into the air, yet California leaders still haven’t tracked it enough to warrant regulating the pest control industry with new alternatives—and both pieces of information should be alarming.